The Digital Carbon Footprint is Growing!
It’s not just transportation or shopping, but also browsing websites and sending emails that increase your carbon footprint.
Every digital device consumes energy, which leads to CO2 emissions. This can be measured and reduced.
How Big is Your Website’s Carbon Footprint?
You only need 3 pieces of information to find out:

The URL of the site
you want to measure

The % of returning visitors (they leave a smaller footprint)

And the country where
the visitors are coming from

Make Your Website More Sustainable!
Every time a web page loads, energy is consumed. The data transfer required to display images, videos, and text significantly contributes to the global CO2 emissions as part of your digital carbon footprint. Reducing your carbon footprint is not only an eco-friendly solution but also improves your site’s energy efficiency. Less energy is required to load your pages, which makes browsing faster, greener, and enhances the user experience for your visitors.
Discover how you can reduce your website’s energy costs and carbon footprint - all at once!
References
Our partners in reducing the digital carbon footprint
Carbon.Crane
Let’s Reduce the Digital Carbon Footprint Together!
The Carbon.Crane team, made up of data scientists and digital communications experts, leverages artificial intelligence to develop solutions that reduce carbon emissions and energy consumption - without compromising efficiency or user experience.
GET TO KNOW US
Our solutions
Our intuitive dashboards allow you to monitor and analyze the carbon footprint of your e-mail campaigns and websites. Beyond measurement, E-mail Carbon Monitor® and Website Carbon Monitor® provide you with multiple solutions to reduce your carbon emissions.
Optimize the carbon efficiency of your website
Website Carbon Monitor® provides a comprehensive and detailed overview of the carbon efficiency of your website, which can be easily reviewed and analyzed on a user-friendly interface. By analyzing incoming traffic and its flow within your website, it reveals your options for reducing carbon emission and models their effectiveness in several scenarios.
FIND OUT MORE
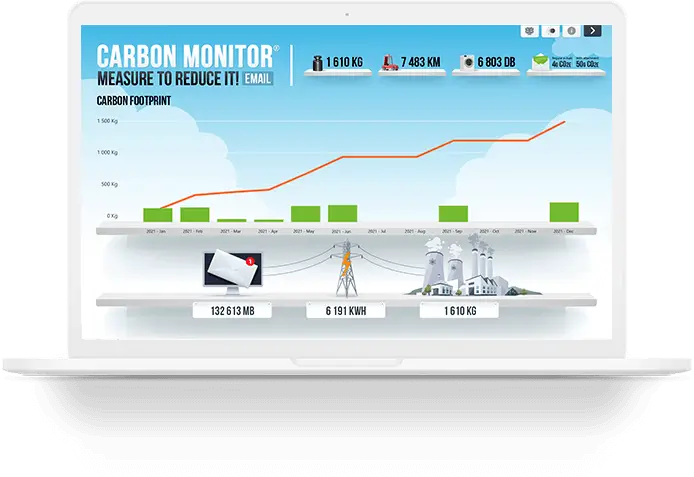
Reduce the carbon footprint of your eDM campaigns
The overview and analytical views of E-mail Carbon Monitor® display the carbon efficiency of your e-mail campaigns. Carbon Ratio® indicates the carbon footprint of unnecessarily sent e-mails, and identifies opportunities for reduction, thus supporting both planning and monitoring effectiveness. In addition to individual campaign analysis, the system also allows local and regional comparisons.
FIND OUT MORE


















