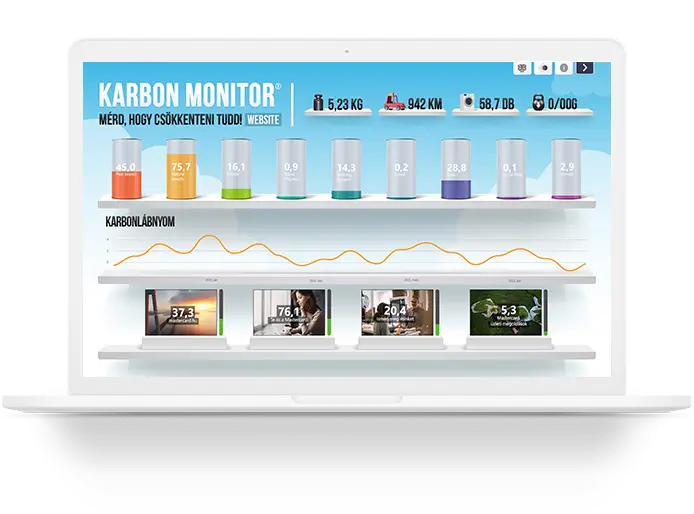
CARBON CALCULATOR
How big is the carbon footprint of your webpage?

0.09 G CO2e /pageload

0.72 Wh /pageload

0.78 ml /pageload
Monthly page views result in the website’s annual carbon emissions of:
828.7 KG
CO2e
Nem Fenntartható
Which corresponds to
1723 km
by car
642
loads of laundry
237
handwashes
NET CO2E EMISSION![]()
1.42 G
The "Diagnostics" view help you better understand the components of the webpage (on the URL above) and their impact on its carbon footprint.
"Impact Analysis" matrix gives the conclusion of adjustment priorities.
Right-up corner is the must-deal-with-it section while Left-bottom oriented items are in the well-done zone.
NUMBER OF COMPONENTS' TYPES
98 pcs
SIZE OF COMPONENTS' TYPES
3.1
Carbon footprint
The carbon footprint of the page
G CO2E
PageView per month
PV/MO
Annual Carbon Emission
KG CO2E
Reduction modelling


Result of reduction
Volume of Reduction
CO2E

Energy saving
Water saving

The website's reduction potential through image optimization
- %
KB
G CO2E
Based on measurements from httparchive, images - and consequently their carbon footprint - would account for approximately 40% (median) the size of web pages.
This tab is to estimate how much smaller images could be without compromising their quality to the human eye.
In other words: To what extent could the images contribute to the reduction potential of the page?
- - - - - Optimal image size benchmark
Light green bubble zone: Reduction potential
Dark green bubble zone: Optimized image size
CARBON COLONY

Diagnostics help us identify components that are responsible for carbon emission.
But do we know who they really are?

The image - or picture, photo - belongs to the larger types of content on websites.

Classification:
It belongs to the family of audio-visual tools.
Distinctive feature:
It is used as an illustration or on its own. As the famous saying goes: a picture is worth a thousand words. It can be poorly compressed.
Occurrence:
It is widely spread, especially favoured by websites publishing product presentations, usage tips, event reports, and news. But they can also be found on websites specifically selling pictures.
Size:
Ranges widely, the smaller ones can be found in sizes as small as 50 KB, while the larger ones can reach several tens of MBs in size.
Footprint:
Due to its size, it can be significant, especially the unnecessarily large ones can be harmful to the environment.
Taming:
Avoid using it in its original size, always optimize it for the website. If necessary, seek expert assistance.


Media is one of the largest existing audio-visual content form on websites.

Classification:
It belongs to the family of audio-visual content elements.
Distinctive feature:
Simultaneous displaying sound and moving images so conveying message. Addictive. It can be ineffectively compressed.
Occurrence:
It is widely spread, particularly favouring websites that showcase product demonstrations, usage tips, event reports, and news.
Size:
It varies widely, with larger ones reaching several hundred megabytes in size.
Footprint:
Due to its size, it can have significant carbon emissions, especially full-screen, automatically playing instances that can be harmful to the environment.
Taming:
Avoid embedding it directly into the webpage; it is recommended to include it as a link within the content of the page. Please seek expert assistance.

Font or font style, character set used in the design and layout of the website.

Classification:
It belongs to the family of tools that determine the visual appearance.
Distinctive feature:
They give atmosphere and style to the page, therefore, in addition to the given system fonts, there are separate personalities, i.e. unique font sets. They are sensitive to the environment, if they feel like it, they don't always appear as expected (especially accents)
Occurrence:
Everywhere within a website, they can even be of several types and of different sizes within one page.
Size:
Ranges widely, the smaller ones can be found in sizes as small as 50 KB, while the larger ones can reach several tens of MBs in size.
Footprint:
The unique font gets itself invited to the website from its own server, so its carbon emissions are also higher.
Taming:
Individual fonts are nice, but it is worth choosing system fonts instead (pay attention to this when designing the image), or font streaming, i.e. refer to them in the central storage of Google Font.


A template that defines the style of the website, a stylist who describes the appearance of the page.

Classification:
It belongs to the family of tools that determine the visual appearance.
Distinctive feature:
They have good taste and are of two types: internal (in the HTML document) and external (in the CSS file referenced by the HTML). Their size can be affected by how many and how complex formatting rules they contain.
Occurrence:
You can find it in HTML or XHTML documents.
Size:
Basically, it is not a big file (10K-1Mb), it depends on the type.
Footprint:
If the style sheet refers to the rule from an external source, its carbon emissions can also become significant.
Taming:
Selecting and using only those style elements from the style description "library" that are really necessary for the appearance of the elements on the page.


Quite a character: the HTML file of the completed page is the one that describes what should be displayed in what structure and system - header-body-footer.

Classification:
It belongs to the family of documents that determine the visual appearance.
Distinctive feature:
It is unavoidable, there is no page without it. And he knows about himself.
Occurrence:
Look for the page on the server responsible for hosting.
Size:
Typically, it is not very large (a few approx. - 100-200 kb) because it contains links.
Footprint:
Based on its size, not too big, but it can be optimised.
Taming:
If the developers work with a template or ready-made system document, it is worth leaving only the necessary elements.

It is constantly conducting: actually a series of instructions to perform a specific operation, automate a task or manipulate data.

Classification:
It belongs to the family of documents defining the operation.
Distinctive feature:
They are tasked with repetitive operations and can be simple or very complex depending on the requirements. Certain programming languages are called scripting languages, such as Perl or Javascript.
Occurrence:
It is widely spread, especially favoured by websites publishing product presentations, usage tips, event reports, and news. But they can also be found on websites specifically selling pictures.
Size:
Part of the program, look for it there!
Footprint:
The larger the file size, the greater the carbon emission - if there are many of them, their emission can become significant due to their number (e.g. they are just overflowing on advertising pages).
Taming:
With general technology, everything is included - it's worth choosing what is actually needed - but it's a big challenge for programmers, they won't love you for it.
Download the results:


Website Badge®
Websites that use Carbon.Crane's Website Carbon Monitor® are entitled to place this badge in their footer which shows that they are consciously and actively working to reduce their website's carbon footprint—in partnership with Carbon.Crane.